Novelty and non-obviousness requirements for patentability are assessed based on the contents of the “prior art”, which can include information previously published by anyone—even by an inventor. Section 102 of the patent laws formally defines what qualifies as prior art in the USA. An earlier “printed publication” will usually count as prior art for novelty (anticipation) and obviousness assessments against a later patent application. Though there are some exceptions, including a one-year grace period that may exclude prior disclosures by an inventor.
The question at hand is about the legal requirements for something to qualify as a “printed publication” for patentability in the U.S. (since the adoption of the America Invents Act [AIA]) This mostly depends on whether relevant technical disclosures appeared in something was generally publicly accessible long enough ago. For the discussion that follows, we will simply assume that given materials contain some kind of relevant technical disclosure.
Examples of Printed Publications
Printed publications can be all sorts of things. They can include books, technical journal articles, web pages, videos, audio recordings, etc. This type of prior art is not limited to the particular format of the materials. In the Internet age, printed publications encompass more than just written text, and more than just hard copy materials.
But “printed publications” generally exclude products themselves. That is, a commercial product or the public use of a method/process would not normally be considered a “printed publication”, although they might instead fall within on-sale and/or public use prior art categories. Yet associated product manuals, product advertisements, and the like might qualify as printed publications.
“Printed Publications” Versus a “Patent” or “Application for Patent Published or Deemed Published”
Before going any further, it is important to note that U.S. law calls out patents and published patent applications separately from “printed publications”. (35 U.S.C. § 102(a)). But patents and published patent applications can be considered “printed publications” too. Patent-related publications can potentially qualify as prior art as any (or all) of a “printed publication”, something “patented,” and/or as a “a patent issued under section 151, or in an application for patent published or deemed published under section 122(b).” In other words, those categories are not mutually exclusive.
The important point here, which may be counter-intuitive, is that “printed publications” include but also go beyond patent-related publications. For that reason, the term “non-patent literature” (NPL) is sometimes used to describe a typical kind of non-patent prior art that falls under the category of printed publications. That terminology sometimes helps to highlight unique issues that can arise when seeking to establish that an NPL reference qualifies as prior art.
Public Accessibility
The first question in determining if something qualifies as a printed publication is determining whether it was published. Courts have said that “public accessibility” is the touchstone in determining whether a reference constitutes a “printed publication”. A given reference will be considered publicly accessible only if it was made available to the extent that persons interested and ordinarily skilled in the relevant subject matter (or art) exercising reasonable diligence can locate it. There is no formula or checklist for making that determination. Whether a reference is publicly accessible is determined on a case-by-case basis based on all the facts and circumstances surrounding disclosure of the reference to members of the public.
There are really three ways something can be established as publicly accessible in the eyes of U.S. courts:
- Cataloging/indexing – By establishing that a document was catalogued or indexed in a publicly accessible archive (e.g., a library catalog or Internet search engine) so that persons interested and ordinarily skilled in the subject matter or art can locate it by exercising reasonable diligence and using available research tools, regardless of whether anyone actually accessed it;
- Distribution/dissemination – By establishing that a document was distributed or disseminated (e.g., mailed, handed out in person, sent in a newsgroup electronic message, or announced orally at a conference and made available) in a sufficiently broad way, without a reasonable expectation of privacy, so that members of the public interested in and ordinarily skilled in the subject matter or art could obtain copies by exercising reasonable diligence; or
- Public display (without literal distribution) – By establishing that materials (e.g., a temporarily displayed slide presentation, video shown on-site, poster, billboard, etc.) were publicly displayed for a sufficient time and in a sufficiently broad manner, without a reasonable expectation of privacy, so as to be sufficiently accessible to persons interested and ordinarily skilled in the subject matter or art by exercising reasonable diligence, even though copies of the materials were never distributed or indexed and the materials never physically left the presenter’s control.
Notably, courts have said that a sufficient public dissemination or display of materials can make them a “printed publication” even where those materials were never searchable and never indexed/cataloged. Cataloging or indexing something is just one among many ways that something can be considered published and publicly available.
Private communications do not count as printed publications, whether designed for the use of single persons or of a few restricted groups of persons. Anything that is reasonably expected to remain secret, such as private communications marked as confidential or not for distribution or exchanged under a non-disclosure agreement (NDA), will not qualify as printed publication prior art. Although, sometimes courts disregard ambiguous confidentiality restrictions or read alleged confidentiality terms narrowly to still find public accessibility. When dissemination or display is asserted as the basis for public accessibility, it is necessary to look at certain factors to determine the reference was sufficiently publicly accessible to count as a “printed publication”. For instance, establishing public display requires looking at where and how the display occurred, including the openness, size, and nature of the display venue.
Also, technical accessibility alone is not enough if no one of ordinary skill in the art could have reasonably found the materials except by accident. The materials have to sufficiently publicly accessible to be considered “published”, by doing something that reasonably alerts the relevant public to their existence. Materials that are in a library or on web server, or randomly left lying in a public place, but that have not been indexed, disseminated to, or otherwise affirmatively announced to the interested public will not be considered generally publicly accessible, for example.
It may be helpful to consider a push vs. pull distinction regarding the public accessibility threshold. Publication in effect requires that materials be pushed out in some manner that allows the interested public to know about them. Such a “push” could be any of the three options described above: cataloging/indexing, public dissemination, or public display. An interesting facet of this is that anyone can publish a “printed publication.” There is no hierarchy of worthy/unworthy publications. Publication is not limited to certain channels (controlled by gatekeepers). But the mere fact that someone could “pull” information by specifically requesting it is not enough. It begs the question to say that information could be requested if there was no reason for someone to know in the first place that it could (technically) be requested. In short, printed publication status for patentability requires some kind of “push” out of the realm of private knowledge and into the realm of public accessibility.
Date of Public Availability
In order to qualify as prior art against a given claim, a printed publication must also be old enough. The essence of something being “prior art” is that it pre-dated a later effort to patent an invention. This requires looking whether a given publication was publicly accessible (published) before a critical date. The term “critical date” is often used in order to implicitly acknowledge that the date that divides prior art from things that are not old enough to be prior art varies depending on whether or not an exception applies—possible exceptions are discussed below. For a typical “printed publication” by a third party, where no exception applies, the critical date means before the effective filing date of the patent claim at issue.
The date of public availability is sometimes easily determined, but not always. This question is easiest when the materials in question are the kind subject to a predictable and reliable means of publication. For instance, using a U.S. patent application publication as a “printed publication” is straightforward because the patents are official U.S. government documents that are publicly available from the time they are issues and the issue dates printed on the face of patents are reliable indicators of the actual date of issuance (publication). This question is also fairly easy for foreign patent documents.
When in comes to many types of materials, however, dates may not appear on the materials themselves or those dates might not be sufficiently reliable. To use a famous example, Sigmund Freud’s book Die Traumdeutung [The Interpretation of Dreams] was first published in November of 1899 but the title page was post-dated to 1900. Also, dates appearing on a document may indicate something other than a date of general public accessibility. For example, the mere presence of a copyright notice date, printing date, Internet server upload date, or the like on reference itself will not necessarily satisfy public availability evidentiary requirements. But publication by an “established” publisher on something bearing traditional hallmarks of publication (a book’s ISBN, etc.) may be sufficient in AIA trials before the USPTO’s Patent Trial & Appeal Board (PTAB).
There can also be disputes about revisions or different versions of a given publication. This is especially true for online materials. Sometimes a publication date may reflect only the initial publication date. But it may not account for the dates that revisions, modifications, or later additions took place. The date of public accessibility is assessed on the basis of the particular version put forward as potential prior art, and cannot be assumed to match that of a substantively different version.
Legal Standards for Evidence of Publication
To complicate matters, use of “printed publication” evidence in formal patent examination or disputes requires satisfying rules around the use and introduction of evidence. Different evidentiary standards will apply depending on where and how patentability or validity is being assessed.
During regular examination of a new patent application at the USPTO, a relatively low evidentiary standard is applied. A date appearing on a document can establish its publication for examination purposes unless the applicant challenges it. (MPEP § 2128).
However, higher standards are applied in contentious proceedings, including IPR proceedings and during infringement suits in courts. In those situations, there are rules against hearsay (Fed. R. Evid. 802 and 803) and rules requiring authentication of evidence (Fed. R. Evid. 901 and 902). These requirements may necessitate use of a witness to authenticate something put forward as a “printed publication” and its alleged publication date. This can include testimony from a librarian who cataloged something as of a particular date or a computer forensic expert able to retroactively determine the date of publication.
Web pages are a common type of printed publication evidence for which the publication date normally needs to be established beyond just a date that appears on the web page itself. Aside from witness testimony, demonstrating a clear reliable process for capturing, preserving, and presenting the web page, such as using the Internet Archive’s “Wayback Machine,” might be acceptable. (See https://archive.org/legal/faq.php).
Complicating matters still further is that a preponderance of the evidence standard is applied in all USPTO matters while a higher clear & convincing evidence standard is applied in courts. So the PTAB may accept something as a printed publication while a district court might not, based on these different evidentiary burdens (under essentially the same evidentiary rules).
Potential Exceptions
A printed publication will not count as prior art if (a) it was by an inventor within a one-year grace period before the patent application’s effective filing date or (b) the publication is by another but an inventor had previously publicly disclosed the invention (within the grace period).
“(a) Novelty; Prior Art.-A person shall be entitled to a patent unless-
(1) the claimed invention was patented, described in a printed publication, or in public use, on sale, or otherwise available to the public before the effective filing date of the claimed invention; or
(2) the claimed invention was described in a patent issued under section 151, or in an application for patent published or deemed published under section 122(b), in which the patent or application, as the case may be, names another inventor and was effectively filed before the effective filing date of the claimed invention.
(b) Exceptions.–
(1) Disclosures made 1 year or less before the effective filing date of the claimed invention.-A disclosure made 1 year or less before the effective filing date of a claimed invention shall not be prior art to the claimed invention under subsection (a)(1) if–
(A) the disclosure was made by the inventor or joint inventor or by another who obtained the subject matter disclosed directly or indirectly from the inventor or a joint inventor; or
(B) the subject matter disclosed had, before such disclosure, been publicly disclosed by the inventor or a joint inventor or another who obtained the subject matter disclosed directly or indirectly from the inventor or a joint inventor.
(2) Disclosures appearing in applications and patents.-A disclosure shall not be prior art to a claimed invention under subsection (a)(2) if-
(A) the subject matter disclosed was obtained directly or indirectly from the inventor or a joint inventor;
(B) the subject matter disclosed had, before such subject matter was effectively filed under subsection (a)(2), been publicly disclosed by the inventor or a joint inventor or another who obtained the subject matter disclosed directly or indirectly from the inventor or a joint inventor; or
(C) the subject matter disclosed and the claimed invention, not later than the effective filing date of the claimed invention, were owned by the same person or subject to an obligation of assignment to the same person. [see also § 102(c) regarding inventions under joint research agreements that may satisfy this provision]
35 U.S.C. § 102(a) and (b) (emphasis added)
This rather long list of possible exceptions is no doubt confusing. But some general points may aid in understanding the exceptions.
First, the exceptions under § 102(b) fall into two categories depending on whether the alleged prior art is put forward under § 102(a)(1) or under § 102(a)(2). Here, note that § 102(a)(2) applies only to U.S. patents and published patent applications (plus PCT international application publications designating the U.S.). So any non-patent materials like books, journal articles, web pages, and the like will only be able to qualify as prior art under § 102(a)(1) and only the exceptions under § 102(b)(1) need to be considered. Similarly, any foreign patents or published applications will only be able to qualify as prior art under § 102(a)(1) and only the exceptions under § 102(b)(1) need to be considered.
Second, under the § 102(b)(1) exceptions that apply to a “disclosure in a printed publication,” there are two possibilities: (A) disclosures made by (or on behalf of) an inventor within the one-year grace period, and (B) where an inventor made a qualifying public disclosure that pre-dated the printed publication. Where they apply, these exceptions establish a “critical date” one year before the effective filing date of the inventor’s patent application (assessed claim-by-claim). In practical terms, exception (B) will rarely arise, partly because it requires satisfying exception (A) plus additional requirements. The more common of the two exceptions is that an inventor’s own printed publication disclosures up to one year prior to a new patent application filing will not count against that inventor as prior art in the U.S.
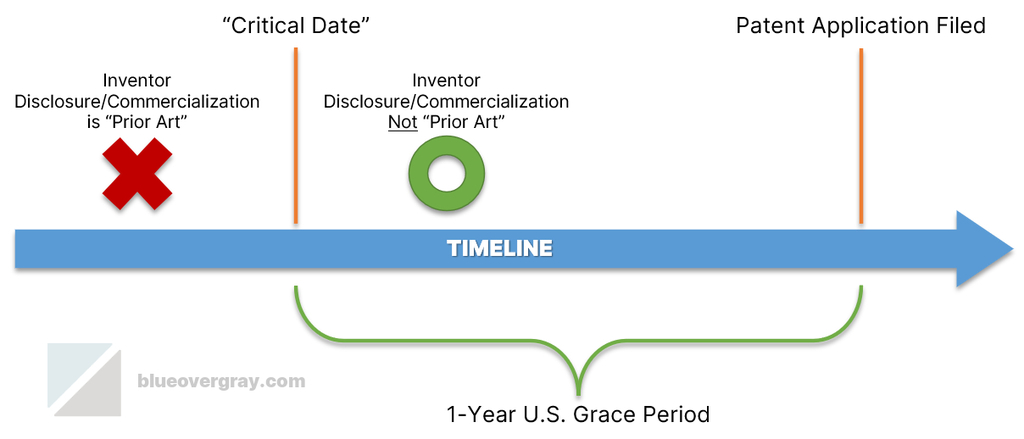
One of the more important aspects of these exceptions is that an inventor’s own prior patent application may not qualify as prior art against that inventors own later application depending on when the prior application is published. This situation can arise when a later application does not formally claim priority to the inventor’s own prior application.
These exceptions to prior art status are rather unique to U.S. patent law. Most other countries follow more of an absolute novelty approach, with no grace period for delayed patent filings. So keep in mind that every jurisdiction will have its own rules for what counts as prior art and those rules offer differ from those in the U.S.

Austen Zuege is an attorney at law and registered U.S. patent attorney in Minneapolis whose practice encompasses patents, trademarks, copyrights, domain name cybersquatting, IP agreements and licensing, freedom-to-operate studies, client counseling, and IP litigation. If you have patent, trademark, or other IP issues, he can help.
